Page 13 - My FlipBook
P. 13
irregularity, they will not attach a new block to it. Rather, they will go
back to an earlier part of the chain that can be trusted and attach it
there. The rejected block becomes an “orphan.” Orphans also result from
situations where two miners solve the proof-of-work problem at the same
time—the network has to choose one of the two blocks, and the rejected
one becomes an orphan. Because of this process, any blockchain user
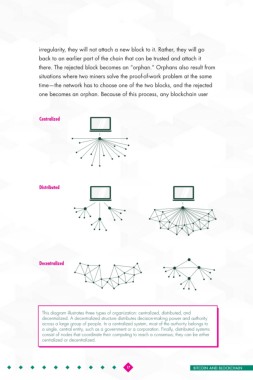
Centralized
Distributed
Distributed
Distributed
Distributed
Distributed
Distributed
De
Decentralizedcentralized
Decentralized
Decentralized
Decentralized
Decentralized
This diagram illustrates three types of organization: centralized, distributed, and
decentralized. A decentralized structure distributes decision-making power and authority
across a large group of people. In a centralized system, most of the authority belongs to
a single, central entity, such as a government or a corporation. Finally, distributed systems
consist of nodes that coordinate their computing to reach a consensus; they can be either
centralized or decentralized.
17 BITCOIN ANd BLOCKCHAIN